Column Filters
Filters can be configured under each column.
Usage
The filters must be declared inside the array returned in the 'filters' method.
To use, you must use the Facade Filter, passing the column you want to apply the filter and the field that will filter.
Filter::multiSelect('category_name', 'category_id')
category_name: Column name defined in Column::field()
category_id: Column name defined in Column::field() or Column dataField
Example:
use PowerComponents\LivewirePowerGrid\Facades\Filter;
public function addColumns(): PowerGridColumns
{
return PowerGrid::columns()
->addColumn('category_id', fn ($dish) => $dish->category_id)
->addColumn('category_name', fn ($dish) => $dish->category->name);
}
public function columns(): array
{
return [
Column::make('Category Name', 'category_name'),
]
}
public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::multiSelect('category_name', 'category_id')
->dataSource(Category::all())
->optionValue('id')
->optionLabel('name'),
];
}use PowerComponents\LivewirePowerGrid\Facades\Filter;
public function addColumns(): PowerGridColumns
{
return PowerGrid::columns()
->addColumn('category_id', fn ($dish) => $dish->category_id)
->addColumn('category_name', fn ($dish) => $dish->category->name);
}
public function columns(): array
{
return [
Column::make('Category Name', 'category_name'),
]
}
public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::multiSelect('category_name', 'category_id')
->dataSource(Category::all())
->optionValue('id')
->optionLabel('name'),
];
}Result:
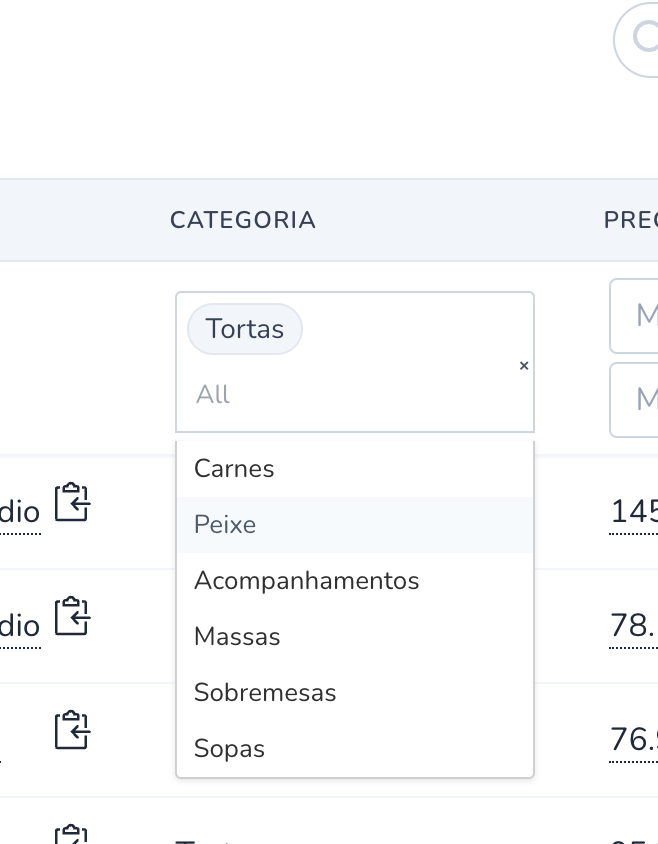
Available filters:
- Filter::inputText
- Filter::select
- Filter::enumSelect
- Filter::boolean
- Filter::datepicker
- Filter::multiSelect
- Filter::multiSelectAsync
- Filter::dynamic
Customize query & collection return
You can customize your results using constructors and collection methods by passing a closure function
- Each filter contains two methods: builder and collection.
WARNING
When you use the builder or collection methods, you are taking control of the filter.
- Builder example:
->builder(function (Builder $query, mixed $value) {
return $query->where('qty', '>', 10);
})->builder(function (Builder $query, mixed $value) {
return $query->where('qty', '>', 10);
})- Collection example:
->collection(function (Collection $collection, mixed $value) {
return $collection->where($field, '!=', $value);
})->collection(function (Collection $collection, mixed $value) {
return $collection->where($field, '!=', $value);
})- Complete example:
use PowerComponents\LivewirePowerGrid\Facades\Filter;
Filter::boolean('in_stock')
->label('yes', 'no')
->builder(function (Builder $query, string $value) {
return $query->where('in_stock', $value === 'true' ? 1 : 0);
}),use PowerComponents\LivewirePowerGrid\Facades\Filter;
Filter::boolean('in_stock')
->label('yes', 'no')
->builder(function (Builder $query, string $value) {
return $query->where('in_stock', $value === 'true' ? 1 : 0);
}),Custom view components
You can add your own view component using the component method.
- This will render all attributes needed to generate a working custom filter in PowerGrid (such as wireui),
- Pass the extra attributes in the second parameter. (wire:model, class ...).
$attributes = [
'class' => 'p-2',
// ...
];
Filter::boolean('in_stock')
->component('my-custom-select', $attributes)$attributes = [
'class' => 'p-2',
// ...
];
Filter::boolean('in_stock')
->component('my-custom-select', $attributes)TIP
To use the default PowerGrid attributes, check in $attributes->getAttributes()
views/components/my-custom-select.blade.php
<div>
@json($attributes->getAttributes())
<input {{ $attributes->get('inputAttributes') }} />
</div><div>
@json($attributes->getAttributes())
<input {{ $attributes->get('inputAttributes') }} />
</div>Filter methods
These methods enable input for filters at your column header.
Filter::inputText
| Parameter |
|---|
| (string) $column |
| (string) $field |
Methods:
->operators(array $operators)
- Empty - All operators will be loaded
- Only
contains- Will hide the select and keep only the input text- Ex:
->operators(['contains'])
- Ex:
- Some - You will be able to select some operators
- Ex:
->operators(['contains', 'is_not'])
- Ex:
| Available Operators |
|---|
| contains |
| contains_not |
| is |
| is_not |
| starts_with |
| ends_with |
| is_empty |
| is_not_empty |
| is_null |
| is_not_null |
| is_blank |
| is_not_blank |
Example:
public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::inputText('name', 'name')
->operators(['contains', 'is', 'is_not']),
];
}public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::inputText('name', 'name')
->operators(['contains', 'is', 'is_not']),
];
}Result:
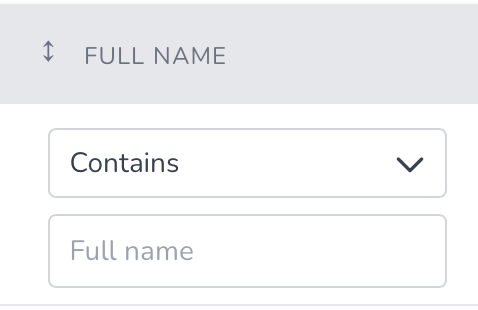
Filter::select
Includes a specific field on the page to filter a hasOne relation in the column.
| Parameter |
|---|
| (string) $column |
| (string) $field |
Methods:
->dataSource(Collection|array|Closure $collection): parameter must be a Datasource.->optionValue(string $value): datasource field name to be displayed in options.->optionLabel(string $value): field used by the filter.
Example:
public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::select('serving_at', 'serving_at')
->dataSource(Dish::servedAt())
->optionValue('serving_at')
->optionLabel('serving_at'),
];
}public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::select('serving_at', 'serving_at')
->dataSource(Dish::servedAt())
->optionValue('serving_at')
->optionLabel('serving_at'),
];
}Result:

Select filter with labels
In some cases, you might want to change the displayed label for each option in your select filter.
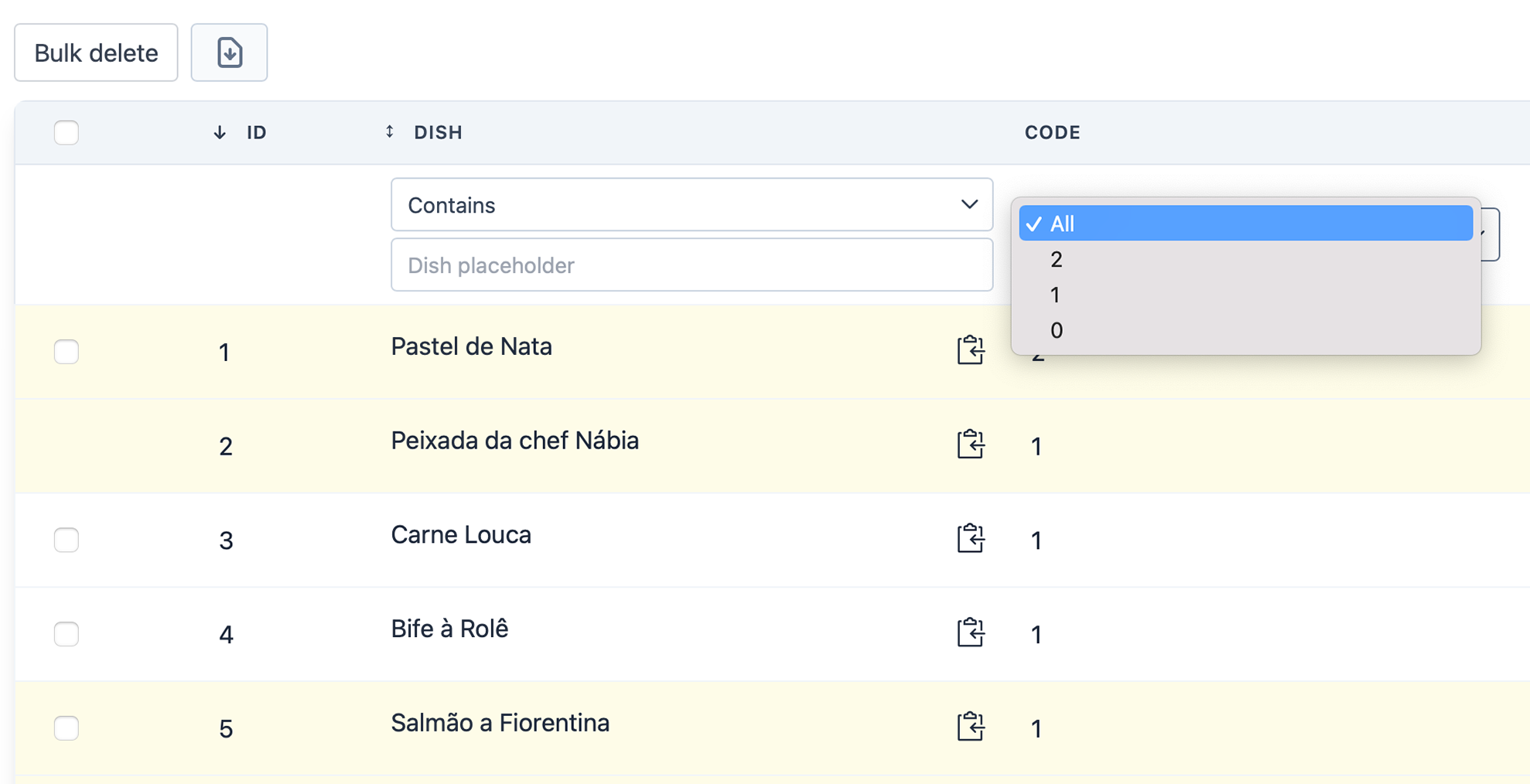
For example, imagine a column code which holds numeric values representing certain product conditions.
The code 0 represents "Best before", 1 represents "Expiring" and 2 represents "Expired".
To build a table with a filter based on Database values, you can use:
public function addColumns(): PowerGridColumns
{
return PowerGrid::columns()
//...
->addColumn('code');
}
public function columns(): array
{
return [
//...
Column::make('Code', 'code'),
];
}
public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::select('code', 'code')
->dataSource(Dish::select('code')->distinct()->get())
->optionValue('code')
->optionLabel('code'),
];
}
public function addColumns(): PowerGridColumns
{
return PowerGrid::columns()
//...
->addColumn('code');
}
public function columns(): array
{
return [
//...
Column::make('Code', 'code'),
];
}
public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::select('code', 'code')
->dataSource(Dish::select('code')->distinct()->get())
->optionValue('code')
->optionLabel('code'),
];
}However, it results in very non-user-friendly Table:
Let's see a full example:
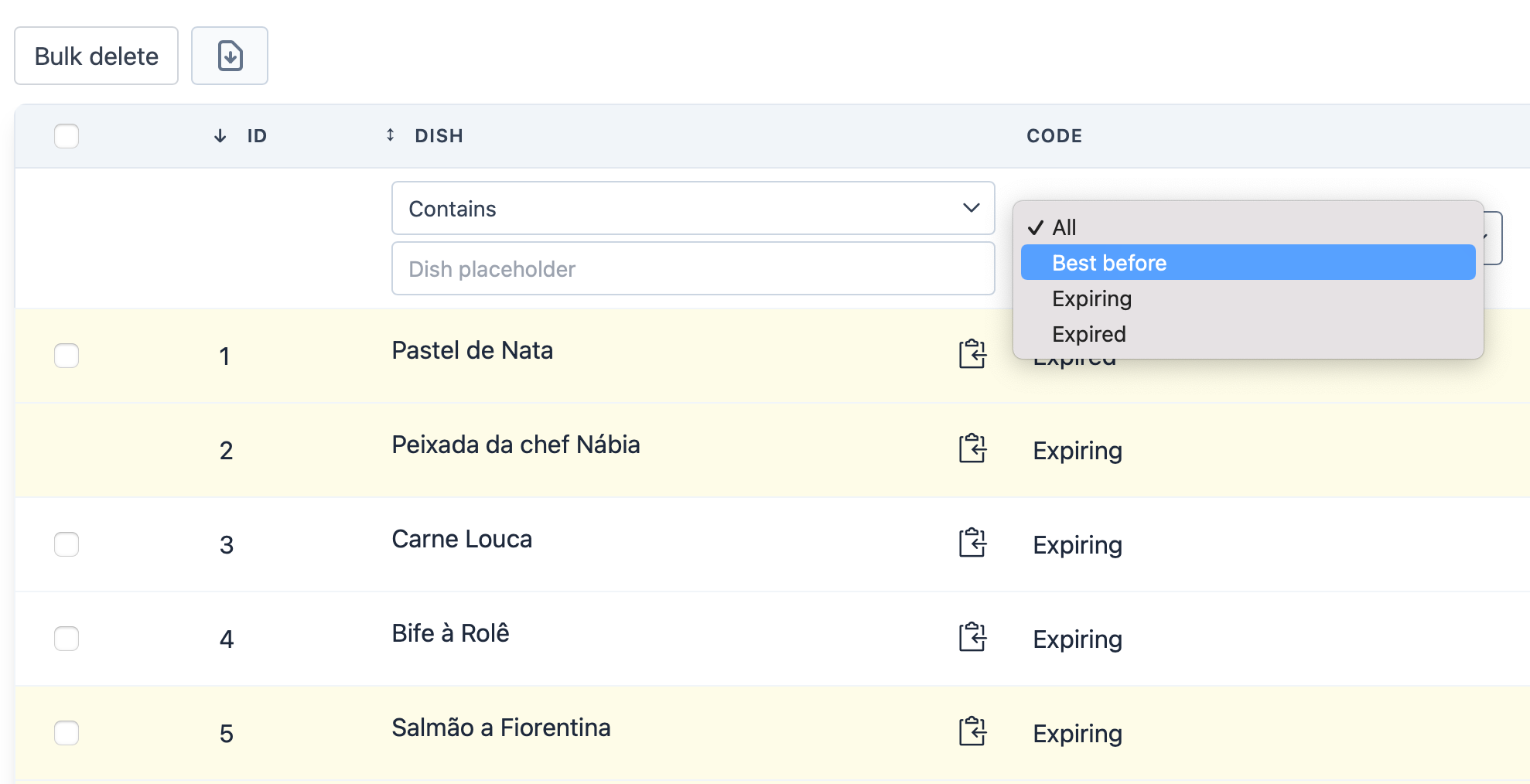
First, let's create a method in Dish Model which will return a collection containing each code with the respective label.
This is very convenient as we can refer to it any time we need access to our product codes.
// File: app/Models/Dish.php
<?php
class Dish extends Model
{
//...
public static function codes()
{
return collect(
[
['code' => 0, 'label' => 'Best before'],
['code' => 1, 'label' => 'Expiring'],
['code' => 2, 'label' => 'Expired'],
]
);
}
}// File: app/Models/Dish.php
<?php
class Dish extends Model
{
//...
public static function codes()
{
return collect(
[
['code' => 0, 'label' => 'Best before'],
['code' => 1, 'label' => 'Expiring'],
['code' => 2, 'label' => 'Expired'],
]
);
}
}Now, we can use this method in DishTable to access our collection of codes.
public function addColumns(): PowerGridColumns
{
return PowerGrid::columns()
/*
Returns the 'label' key of the first collection item matching the database value in column "code"
*/
->addColumn('code_label', fn ($dish) => Dish::codes()->firstWhere('code', $dish->code)['label'])
->addColumn('code');
}
public function columns(): array
{
return [
//...
Column::add()
->title('code')
->field('code_label', 'code'),
];
}
public function filters(): array
{
/*
Uses the codes collection as datasource for the options with the key "label" as the option label.
*/
return [
Filter::select('code', 'code')
->dataSource(Dish::codes())
->optionValue('label')
->optionLabel('code'),
];
}
public function addColumns(): PowerGridColumns
{
return PowerGrid::columns()
/*
Returns the 'label' key of the first collection item matching the database value in column "code"
*/
->addColumn('code_label', fn ($dish) => Dish::codes()->firstWhere('code', $dish->code)['label'])
->addColumn('code');
}
public function columns(): array
{
return [
//...
Column::add()
->title('code')
->field('code_label', 'code'),
];
}
public function filters(): array
{
/*
Uses the codes collection as datasource for the options with the key "label" as the option label.
*/
return [
Filter::select('code', 'code')
->dataSource(Dish::codes())
->optionValue('label')
->optionLabel('code'),
];
}The example above results in a much more user-friendly table:
Filter::enumSelect
Includes a select filter based in a PHP Enum.
| Parameter |
|---|
| (string) $column |
| (string) $field |
Methods:
->dataSource(Collection|array $enumCases): Diet::cases()->optionValue(string $value): datasource field name to be displayed in options.->optionLabel(string $value): field used by the filter.
Example:
public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::enumSelect('diet', 'dishes.diet')
->dataSource(\App\Enums\Diet::cases())
->optionLabel('dishes.diet'),
];
}public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::enumSelect('diet', 'dishes.diet')
->dataSource(\App\Enums\Diet::cases())
->optionLabel('dishes.diet'),
];
}Consider the following Enum with Dietary restrictions.
The database field diet contains the int values (0, 1 or 2). In this Enum we added a method label() to display a human friendly value for each case.
<?php
enum Diet: int
{
case ALL = 0;
case VEGAN = 1;
case CELIAC = 2;
public function labels(): string
{
return match ($this) {
self::ALL => "🍽️ All diets",
self::VEGAN => "🌱 Suitable for Vegans",
self::CELIAC => "🥜 Suitable for Celiacs",
};
}
}<?php
enum Diet: int
{
case ALL = 0;
case VEGAN = 1;
case CELIAC = 2;
public function labels(): string
{
return match ($this) {
self::ALL => "🍽️ All diets",
self::VEGAN => "🌱 Suitable for Vegans",
self::CELIAC => "🥜 Suitable for Celiacs",
};
}
}In PowerGrid you can make use of closures to display your Enum labels instead of the default database values.
Including the column with filter:
//...
// Including column
Column::make('Dieta', 'diet', 'dishes.diet'),//...
// Including column
Column::make('Dieta', 'diet', 'dishes.diet'),Result:
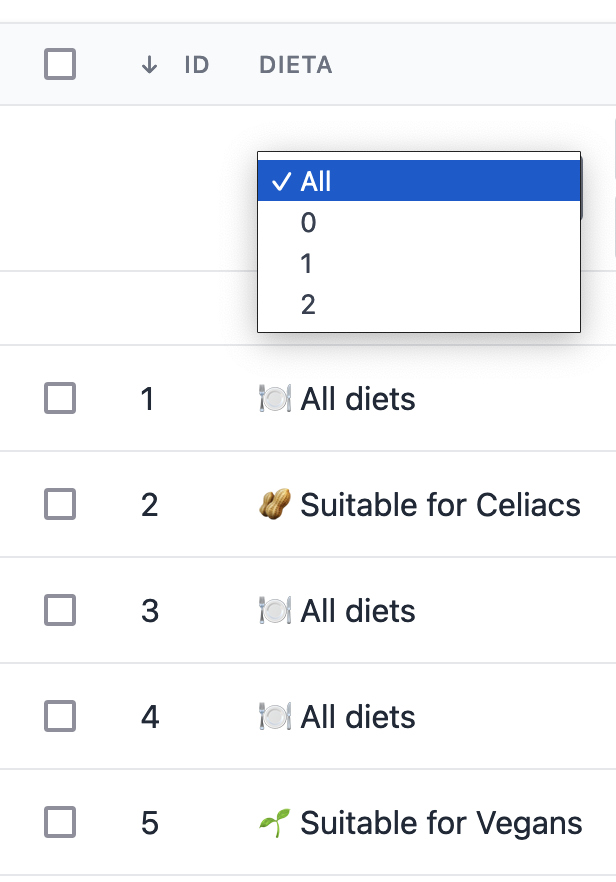
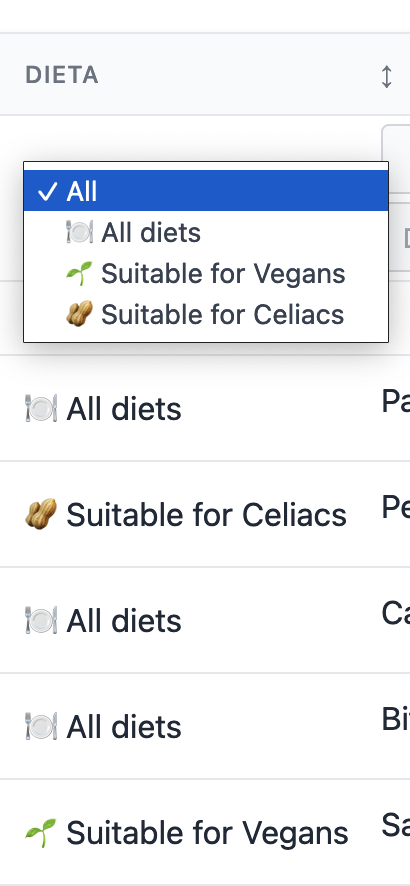
To display your labels instead of case values, you can inlcude the labelPowergridFilter method inside your enum.
<?php
enum Diet: int
{
//...
/**
* Sends labels to PowerGrid Enum Input
*
*/
public function labelPowergridFilter(): string
{
return $this->labels();
}
}<?php
enum Diet: int
{
//...
/**
* Sends labels to PowerGrid Enum Input
*
*/
public function labelPowergridFilter(): string
{
return $this->labels();
}
}
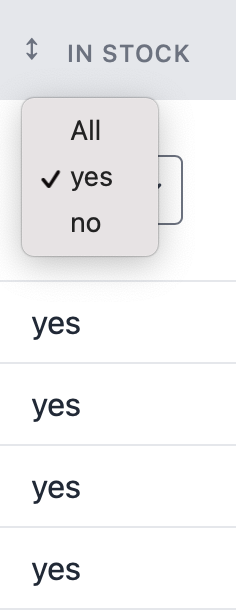
Filter::boolean
Adds a filter for boolean values.
| Parameter |
|---|
| (string) $column |
| (string) $field |
Methods:
->label(string $trueLabel, string $falseLabel): set labels to be displayed fortrueandfalse(E.g, 'Active'/'Inactive')
Example:
public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::boolean('in_stock')
->label('yes', 'no')
];
}public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::boolean('in_stock')
->label('yes', 'no')
];
}Result:
Filter::datetimepicker
- Install
npm i flatpickr --savenpm i flatpickr --save- Configure
Add in app.js
import flatpickr from "flatpickr";import flatpickr from "flatpickr";Add in app.css
@import "flatpickr/dist/flatpickr.min.css";@import "flatpickr/dist/flatpickr.min.css";Includes a specific field on the page to filter between the specific date in the column (datetime format).
Set the language in the config/livewire-powergrid.php file as in the example according to your config/app - locale.
'plugins' => [
// ..
'flatpickr' => [
// ..
'locales' => [
'pt_BR' => [
'locale' => 'pt',
'dateFormat' => 'd/m/Y H:i',
'enableTime' => true,
'time_24hr' => true,
],
'uk' => [
'locale' => 'uk',
'dateFormat' => 'd/m/Y',
'enableTime' => false,
'time_24hr' => true,
],
],
],
], 'plugins' => [
// ..
'flatpickr' => [
// ..
'locales' => [
'pt_BR' => [
'locale' => 'pt',
'dateFormat' => 'd/m/Y H:i',
'enableTime' => true,
'time_24hr' => true,
],
'uk' => [
'locale' => 'uk',
'dateFormat' => 'd/m/Y',
'enableTime' => false,
'time_24hr' => true,
],
],
],
],| Parameter |
|---|
| (string) $column |
| (string) $field |
Methods:
->params(array $collection): Params must be passed as "key => value". Available keys are:'only_future' => true: Will not allow to select dates in the past.'no_weekends' => true: Will not allow to select weekends.'timezone' => 'America/Sao_Paulo': Parse the searched date with the specified timezone.
Example:
public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::datepicker('produced_at_formatted', 'produced_at'),
];
}public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::datepicker('produced_at_formatted', 'produced_at'),
];
}Result:
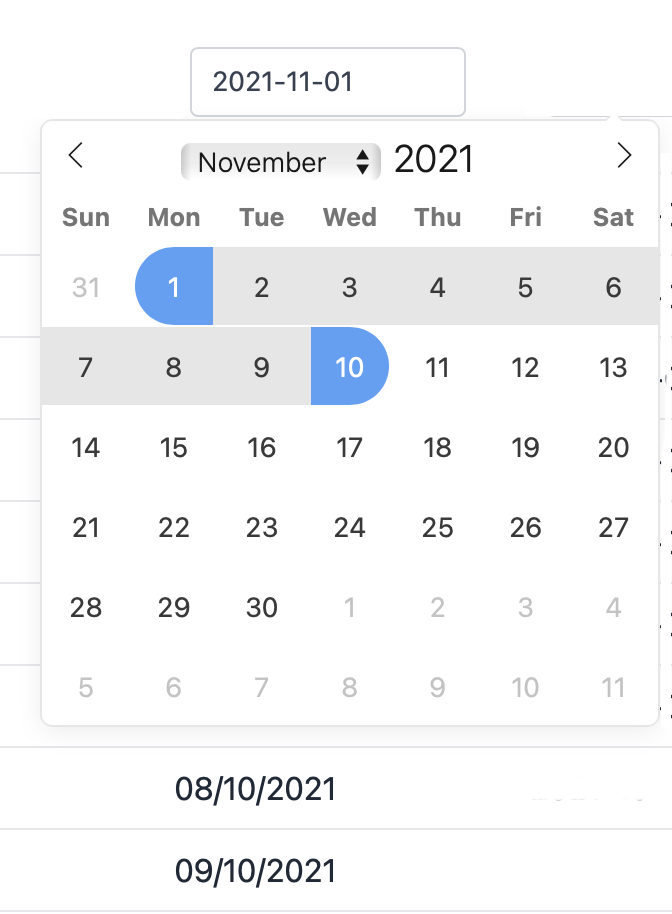
Filter::datepicker
Unlike datetimepicker, datetime to filter on column in 'date' format. Inherits all attributes from datetimepicker
Filter::multiSelect
Includes a specific field on the page to filter a hasOne relation in the column.
To use the multiSelect filter you must choose which frontend framework will be responsible for rendering the selector between TomSelect or SlimSelect.
Using SlimSelect
- Install
npm i slim-selectnpm i slim-select- Configure
Add in app.js
import SlimSelect from 'slim-select'
window.SlimSelect = SlimSelectimport SlimSelect from 'slim-select'
window.SlimSelect = SlimSelectAdd in app.css
@import "~slim-select/dist/slimselect.css";@import "~slim-select/dist/slimselect.css";change in config/livewire-powergrid.php
'select' => [
'default' => 'slim',
/*
* TomSelect Options
* https://tom-select.js.org
*/
'tom' => [
'plugins' => [
'clear_button' => [
'title' => 'Remove all selected options',
],
],
],
/*
* Slim Select options
* https://slimselectjs.com/
*/
'slim' => [
'settings' => [
'alwaysOpen' => false,
],
],
],'select' => [
'default' => 'slim',
/*
* TomSelect Options
* https://tom-select.js.org
*/
'tom' => [
'plugins' => [
'clear_button' => [
'title' => 'Remove all selected options',
],
],
],
/*
* Slim Select options
* https://slimselectjs.com/
*/
'slim' => [
'settings' => [
'alwaysOpen' => false,
],
],
],Using TomSelect
- Install
npm i tom-selectnpm i tom-select- Configure
Add in app.js
import TomSelect from "tom-select";
window.TomSelect = TomSelectimport TomSelect from "tom-select";
window.TomSelect = TomSelectAdd in app.css
@import "~tom-select/dist/scss/tom-select.bootstrap5";@import "~tom-select/dist/scss/tom-select.bootstrap5";change in config/livewire-powergrid.php
'select' => [
'default' => 'tom',
/*
* TomSelect Options
* https://tom-select.js.org
*/
'tom' => [
'plugins' => [
'clear_button' => [
'title' => 'Remove all selected options',
],
],
],
/*
* Slim Select options
* https://slimselectjs.com/
*/
'slim' => [
'settings' => [
'alwaysOpen' => false,
],
],
],'select' => [
'default' => 'tom',
/*
* TomSelect Options
* https://tom-select.js.org
*/
'tom' => [
'plugins' => [
'clear_button' => [
'title' => 'Remove all selected options',
],
],
],
/*
* Slim Select options
* https://slimselectjs.com/
*/
'slim' => [
'settings' => [
'alwaysOpen' => false,
],
],
],Using
| Parameter |
|---|
| (string) $column |
| (string) $field |
Methods:
->dataSource(array|Collection $collection): parameter must be a Datasource.->optionValue(string $value): datasource field name to be displayed in options.->optionId(string $value): field used by the filter.
Example:
public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::multiSelect('category_name', 'category_id')
->dataSource(Category::all())
->optionValue('id')
->optionLabel('name'),
];
}public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::multiSelect('category_name', 'category_id')
->dataSource(Category::all())
->optionValue('id')
->optionLabel('name'),
];
}Result:

Filter::multiSelectAsync
If you don't want to load the multiselect data immediately when starting the page, you can use this feature, it helps your datatable behave faster. As Powergrid uses TomSelect, set it in settings (here).
WARNING
- Make sure you have TomSelect set up beforehand.
- You must use an external API or create your own endpoint: route, controllers.
Using
| Parameter |
|---|
| (string) $column |
| (string) $field |
Methods:
->dataSource(array|Collection $collection): parameter must be a Datasource.->optionValue(string $value): datasource field name to be displayed in options.->optionId(string $value): field used by the filter.
Async methods:
->url(string $url): API URL used by the filter (See example).->method(string $method = 'get'): API method (get,post ..) used by the filter.->parameters(string $parameters = []): Other options to send in the Body of the request along with the text search
Example:
public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::multiSelectAsync('category_name', 'category_id')
->url(route('category.index'))
->method('POST')
->parameters([0 => 'Luan'])
->optionValue('id')
->optionLabel('name'),
];
}public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::multiSelectAsync('category_name', 'category_id')
->url(route('category.index'))
->method('POST')
->parameters([0 => 'Luan'])
->optionValue('id')
->optionLabel('name'),
];
}API Example
- Route:
Route::post('category', Index::class)->name('category.index');Route::post('category', Index::class)->name('category.index');- API Controller
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers\Api;
use App\Http\Controllers\Controller;
use App\Models\Category;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Database\Eloquent\Builder;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Collection;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class Index extends Controller
{
public function __invoke(Request $request): Collection
{
return Category::query()
->select('id', 'name')
->orderBy('name')
->when($request->search,
fn (Builder $query) => $query
->where('name', 'like', "%{$request->search}%")
)
->get();
}
}<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers\Api;
use App\Http\Controllers\Controller;
use App\Models\Category;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Database\Eloquent\Builder;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Collection;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class Index extends Controller
{
public function __invoke(Request $request): Collection
{
return Category::query()
->select('id', 'name')
->orderBy('name')
->when($request->search,
fn (Builder $query) => $query
->where('name', 'like', "%{$request->search}%")
)
->get();
}
}Result: 
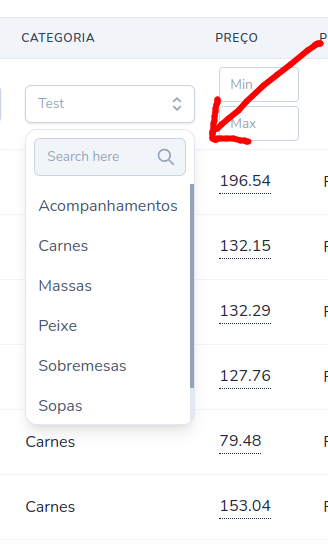
Filter::dynamic
PowerGrid Filters are internal components, if you want to use an external component you can use this functionality. A practical example is when you are using external components (such as wireui) throughout your system and want to apply them in PowerGrid too.
Methods:
->component(string $component): name of component to be rendered: 'x-select' must be 'select'->attributes(array $attributes): extra attributes for the view
Example:
public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::dynamic('in_stock', 'in_stock')
->component('select') // <x-select ...attributes/>
->attributes([
'class' => 'min-w-[170px]',
'async-data' => route('categories.index'),
'option-label' => 'name',
'multiselect' => false,
'option-value' => 'id',
'placeholder' => 'Test',
'wire:model.lazy' => 'filters.select.in_stock'
]),
];
}public function filters(): array
{
return [
Filter::dynamic('in_stock', 'in_stock')
->component('select') // <x-select ...attributes/>
->attributes([
'class' => 'min-w-[170px]',
'async-data' => route('categories.index'),
'option-label' => 'name',
'multiselect' => false,
'option-value' => 'id',
'placeholder' => 'Test',
'wire:model.lazy' => 'filters.select.in_stock'
]),
];
}
Filter by Relationship
To filter by relationships, add each relationship of your main Datasource Table in the relationSearch method.
The relationships must be added in the format:
'model_name' => ['search_column_A', 'search_column_B'...].
Nested singular relationships where both the first relation table's foreign key and the nested relation's primary keys are the Eloquent default can be added in the format:
'model_name' => ['search_column_A', 'nested_model_table' => ['search_column_B', 'search_column_C'].
Example:
public function relationSearch(): array
{
return [
'kitchen' => [ // relationship on dishes model
'name', // column enabled to search
'chef' => ['name'] // nested relation and column enabled to search
],
//...
];
}public function relationSearch(): array
{
return [
'kitchen' => [ // relationship on dishes model
'name', // column enabled to search
'chef' => ['name'] // nested relation and column enabled to search
],
//...
];
}The example above adds the relationship to the kitchen Model and allows the column name to be searched.
 Livewire PowerGrid
Livewire PowerGrid